Maze generation
迷宮生成演算法是一種用於創建迷宮的演算法,其目標是生成一個具有一定難度和趣味性的迷宮。常見的迷宮生成演算法包括深度優先搜索演算法、隨機追踪演算法、分割演算法和Eller's演算法等。
深度優先搜索演算法是一種簡單而有效的迷宮生成演算法。它從一個起始位置開始,在迷宮中隨機選擇一個未訪問的相鄰位置,並將其標記為通過,然後遞歸地探索該位置,直到無法繼續前進為止。然後,回溯回到之前的位置,並選擇另一個未訪問的相鄰位置,重複上述過程,直到所有的位置都被訪問。
以下我們但簡介深度優先搜索法,又叫backtracking。
![]()
1. 準備好格
x1# A demo of backtracking maze generator2
3cols = rows = 204spots = []5
6def setup():7 global spots8 size(630, 630)9 rectMode(CENTER)10
11 for i in range(cols):12 temp = []13 for j in range(rows):14 temp.append(Spot(i, j))15 spots.append(temp)16
17def draw():18 for i in range(cols):19 for j in range(rows):20 spots[i][j].show()21
22class Spot(object):23
24 def __init__(self, _i, _j):25 self.i = _i26 self.j = _j27 self.w = width / (cols + 1 )28 self.h = height / (rows +1 )29 self.x = (self.i+1) * self.w + self.w / 230 self.y = (self.j+1) * self.h + self.h / 231 self.wall = False32
33 def show(self):34 stroke('#555555')35 if self.wall:36 fill('#999999')37 else:38 fill(255)39 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)
跟以往一樣,我們首先準備好格的class。今次比較特別的是,我們會準備n+1格,20x20的話就會是21x21格,因為要為迷宮準備好四面牆。
2. 加入cell class
xxxxxxxxxx851# A demo of backtracking maze generator2
3cols = rows = 204spots = []5cells = []6
7def setup():8 global spots, cells9 size(630, 630)10 rectMode(CENTER)11
12 # create new spots13 for i in range(cols):14 temp = []15 for j in range(rows):16 temp.append(Spot(i, j))17 spots.append(temp)18
19 # create new cells20 for i in range(cols/2):21 temp = []22 for j in range(rows/2):23 temp.append(Cell(i, j))24 cells.append(temp)25 26 # add spots to each cell and add neighbors to each cell27 for i in range(cols/2):28 for j in range(rows/2):29 cells[i][j].addSpots(spots)30 cells[i][j].addNeighbors(cells)31 32
33def draw():34 for i in range(cols):35 for j in range(rows):36 spots[i][j].show()37
38class Spot(object):39
40 def __init__(self, _i, _j):41 self.i = _i42 self.j = _j43 self.w = width / (cols + 1 )44 self.h = height / (rows +1 )45 self.x = (self.i+1) * self.w + self.w / 246 self.y = (self.j+1) * self.h + self.h / 247 self.wall = False48
49 def show(self):50 stroke('#555555')51 if self.wall:52 fill('#999999')53 else:54 fill(255)55 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)56
57class Cell(object):58 # every cell has 4 spots59 def __init__(self, _i, _j):60 self.i = _i61 self.j = _j62 self.cells = [None, None, None, None]63 self.neighbors = []64 self.visited = False65
66 def addSpots(self, _spots):67 #every cell has 4 spots, the bottom right is always wall68 i = self.i69 j = self.j70 self.cells[0] = _spots[i*2][j*2] # top left71 self.cells[1] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2] # top right72 self.cells[2] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2+1] # bottom right73 self.cells[3] = _spots[i*2][j*2+1] # bottom left74 self.cells[2].wall = True75
76 def addNeighbors(self, _cells):77 i = self.i78 j = self.j79 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i-1][j]) if i >0 else None80 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i][j+1]) if j < rows/2-1 else None81 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i+1][j]) if i < cols/2-1 else None82 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i][j-1]) if j >0 else None83
84 def isVisited(self):85 return self.visited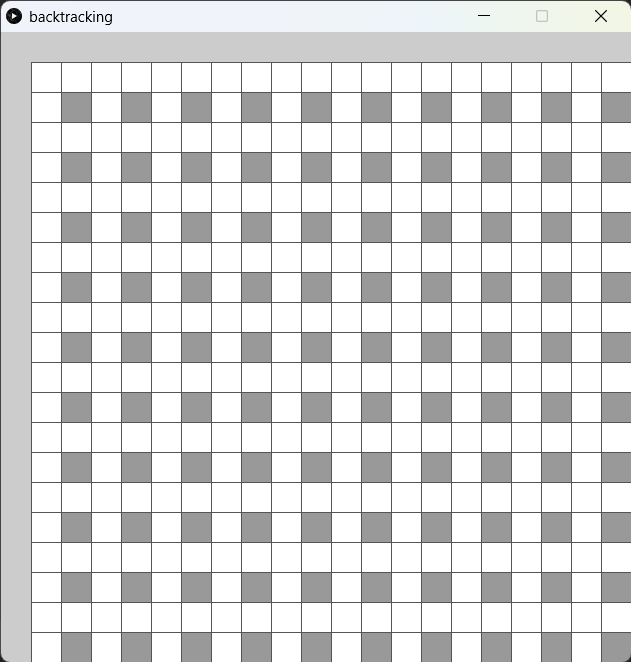
xxxxxxxxxx181class Cell(object):2 # every cell has 4 spots3 def __init__(self, _i, _j):4 self.i = _i5 self.j = _j6 self.cells = [None, None, None, None]7 self.neighbors = []8 self.visited = False9 10 def addSpots(self, _spots):11 #every cell has 4 spots, the bottom right is always wall12 i = self.i13 j = self.j14 self.cells[0] = _spots[i*2][j*2] # top left15 self.cells[1] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2] # top right16 self.cells[2] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2+1] # bottom right17 self.cells[3] = _spots[i*2][j*2+1] # bottom left18 self.cells[2].wall = True新增一個cell class,這個class為迷宮的單元格。每個單元格包含4個spot,表示單元和的四個角落,其中右下角的Spot被標記為牆。
xxxxxxxxxx101 def addNeighbors(self, _cells):2 i = self.i3 j = self.j4 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i-1][j]) if i >0 else None5 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i][j+1]) if j < rows/2-1 else None6 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i+1][j]) if i < cols/2-1 else None7 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i][j-1]) if j >0 else None8
9 def isVisited(self):10 return self.visited此外,每個單元格還包含了一個neighbors列表,表示與該單元格相鄰的單元格。在program2中,程式會將每個Spot添加到相應的單元格中,並且將每個單元格的相鄰單元格添加到neighbors列表中。這種方法可以減少程式生成迷宮時的計算量,提高程式的性能。
xxxxxxxxxx211cols = rows = 202spots = []3cells = []4
5def setup():6 global spots, cells7 size(630, 630)8 #(same as before)9
10 # create new cells11 for i in range(cols/2):12 temp = []13 for j in range(rows/2):14 temp.append(Cell(i, j))15 cells.append(temp)16 17 # add spots to each cell and add neighbors to each cell18 for i in range(cols/2):19 for j in range(rows/2):20 cells[i][j].addSpots(spots)21 cells[i][j].addNeighbors(cells)接著返回主程式,在setup()中,新增cols/2和row/2個cell(因為每4個spot為一個cell,所以只要一半就可以了),接著跟之前一樣幫這此cell加係鄰居。
3. 加入左邊界和右邊界
xxxxxxxxxx1041# A demo of backtracking maze generator2
3cols = rows = 204spots = []5cells = []6wallSpots = []7
8
9def setup():10 global spots, cells, wallSpots11 size(630, 630)12 rectMode(CENTER)13
14 # create the left and top wall15 for i in range(-1, cols):16 wallSpots.append(Spot(i, -1)) 17 for j in range(-1, rows):18 wallSpots.append(Spot(-1, j)) 19
20 # create new spots21 for i in range(cols):22 temp = []23 for j in range(rows):24 temp.append(Spot(i, j))25 spots.append(temp)26
27 # create new cells28 for i in range(cols/2):29 temp = []30 for j in range(rows/2):31 temp.append(Cell(i, j))32 cells.append(temp)33
34 # add spots to each cell and add neighbors to each cell35 for i in range(cols/2):36 for j in range(rows/2):37 cells[i][j].addSpots(spots)38 cells[i][j].addNeighbors(cells)39
40
41def draw():42 # display the wall43 for spot in wallSpots:44 spot.wall = True45 spot.show()46
47 # display the cells48 for i in range(cols):49 for j in range(rows):50 spots[i][j].show()51
52
53class Spot(object):54
55 def __init__(self, _i, _j):56 self.i = _i57 self.j = _j58 self.w = width / (cols + 1)59 self.h = height / (rows + 1)60 self.x = (self.i+1) * self.w + self.w / 261 self.y = (self.j+1) * self.h + self.h / 262 self.wall = False63
64 def show(self):65 stroke('#555555')66 if self.wall:67 fill('#999999')68 else:69 fill(255)70 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)71
72
73class Cell(object):74 # every cell has 4 spots75 def __init__(self, _i, _j):76 self.i = _i77 self.j = _j78 self.cells = [None, None, None, None]79 self.neighbors = []80 self.visited = False81
82 def addSpots(self, _spots):83 # every cell has 4 spots, the bottom right is always wall84 i = self.i85 j = self.j86 self.cells[0] = _spots[i*2][j*2] # top left87 self.cells[1] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2] # top right88 self.cells[2] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2+1] # bottom right89 self.cells[3] = _spots[i*2][j*2+1] # bottom left90 91 self.cells[1].wall = True92 self.cells[2].wall = True93 self.cells[3].wall = True94
95 def addNeighbors(self, _cells):96 i = self.i97 j = self.j98 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i-1][j]) if i > 0 else None99 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i][j+1]) if j < rows/2-1 else None100 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i+1][j]) if i < cols/2-1 else None101 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i][j-1]) if j > 0 else None102
103 def isVisited(self):104 return self.visited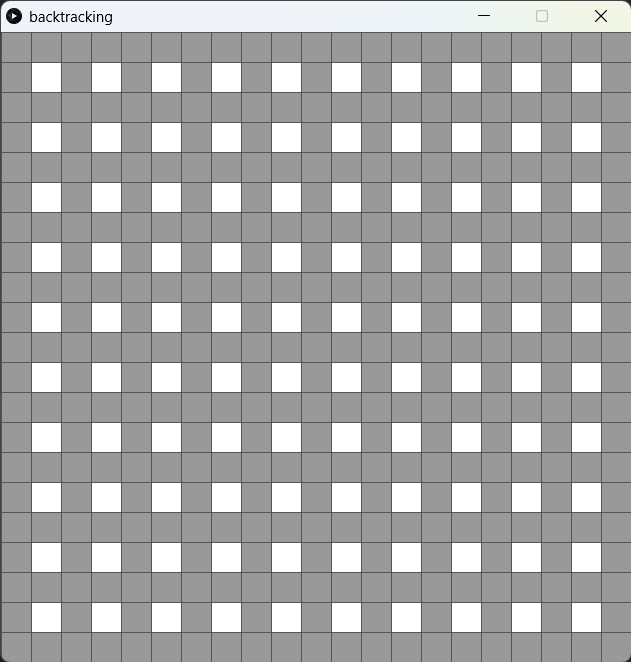
xxxxxxxxxx241# A demo of backtracking maze generator2
3#(same as before)4wallSpots = []5
6
7def setup():8 global spots, cells, wallSpots9 size(630, 630)10 rectMode(CENTER)11
12 # create the left and top wall13 for i in range(-1, cols):14 wallSpots.append(Spot(i, -1)) 15 for j in range(-1, rows):16 wallSpots.append(Spot(-1, j)) 17 18 #(same as before)19
20def draw():21 # display the wall22 for spot in wallSpots:23 spot.wall = True24 spot.show()加入一個wallSpot=[],將左邊界和上邊界都填滿,這是迷宮的四面牆。
xxxxxxxxxx121 def addSpots(self, _spots):2 # every cell has 4 spots, the bottom right is always wall3 i = self.i4 j = self.j5 self.cells[0] = _spots[i*2][j*2] # top left6 self.cells[1] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2] # top right7 self.cells[2] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2+1] # bottom right8 self.cells[3] = _spots[i*2][j*2+1] # bottom left9 10 self.cells[1].wall = True11 self.cells[2].wall = True12 self.cells[3].wall = True此外,在cell class中,在加係spot的同時,除了右下角的Spot被標記為牆以外,右上角和左下角的Spot也被標記為牆。因backtracking演算法是將走過的地方的牆拆除,而不是建牆的。
4. Backtracking
xxxxxxxxxx1611# A demo of backtracking maze generator2
3from random import *4
5cols = rows = 206spots = []7cells = []8wallSpots = []9current = None10stack = []11
12
13def setup():14 global spots, cells, wallSpots, current15 size(630, 630)16 rectMode(CENTER)17 frameRate(10)18
19 # create the left and top wall20 for i in range(-1, cols):21 wallSpots.append(Spot(i, -1)) 22 for j in range(-1, rows):23 wallSpots.append(Spot(-1, j)) 24
25 # create new spots26 for i in range(cols):27 temp = []28 for j in range(rows):29 temp.append(Spot(i, j))30 spots.append(temp)31
32 # create new cells33 for i in range(cols/2):34 temp = []35 for j in range(rows/2):36 temp.append(Cell(i, j))37 cells.append(temp)38
39 # add spots to each cell and add neighbors to each cell40 for i in range(cols/2):41 for j in range(rows/2):42 cells[i][j].addSpots(spots)43 cells[i][j].addNeighbors(cells)44
45 # start from the top left cell46 current = cells[0][0]47 current.visited = True48
49
50def draw():51 global current, stack52
53 # display the wall54 for spot in wallSpots:55 spot.wall = True56 spot.show()57 58 # display the cells59 for i in range(cols):60 for j in range(rows):61 spots[i][j].show()62
63 # display the current cell64 current.highLight()65 66 # generate the maze67 unvisitedNeighbors = current.checkNeighbors()68 if len(unvisitedNeighbors) > 0:69 next = choice(unvisitedNeighbors)70 stack.append(current)71 removeWall(current, next)72 next.visited = True73 current = next74 elif len(stack) > 0:75 current = stack.pop()76 77 78
79def removeWall(a, b):80 x = a.i - b.i81 y = a.j - b.j82
83 if x == 1: # a is on the right of b84 b.cells[1].wall = False85 if x == -1: # a is on the left of b86 a.cells[1].wall = False87 if y == 1: # a is below b88 b.cells[3].wall = False89 if y == -1: # a is above b90 a.cells[3].wall = False91
92
93
94class Spot(object):95
96 def __init__(self, _i, _j):97 self.i = _i98 self.j = _j99 self.w = width / (cols + 1)100 self.h = height / (rows + 1)101 self.x = (self.i+1) * self.w + self.w / 2102 self.y = (self.j+1) * self.h + self.h / 2103 self.wall = False104
105 def show(self):106 stroke('#555555')107 if self.wall:108 fill('#999999')109 else:110 fill(255)111 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)112
113 def highLight(self):114 stroke('#555555')115 fill('#FF0000')116 rect(self.x, self.y, self.w, self.h)117
118
119class Cell(object):120 # every cell has 4 spots121 def __init__(self, _i, _j):122 self.i = _i123 self.j = _j124 self.cells = [None, None, None, None]125 self.neighbors = []126 self.visited = False127
128 def addSpots(self, _spots):129 # every cell has 4 spots, the bottom right is always wall130 i = self.i131 j = self.j132 self.cells[0] = _spots[i*2][j*2] # top left133 self.cells[1] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2] # top right134 self.cells[2] = _spots[i*2+1][j*2+1] # bottom right135 self.cells[3] = _spots[i*2][j*2+1] # bottom left136 137 self.cells[1].wall = True138 self.cells[2].wall = True139 self.cells[3].wall = True140
141 def addNeighbors(self, _cells):142 i = self.i143 j = self.j144 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i-1][j]) if i > 0 else None145 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i][j+1]) if j < rows/2-1 else None146 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i+1][j]) if i < cols/2-1 else None147 self.neighbors.append(_cells[i][j-1]) if j > 0 else None148
149 def isVisited(self):150 return self.visited151
152 def checkNeighbors(self):153 unvisitedNeighbors = []154 for neighbor in self.neighbors:155 if not neighbor.isVisited():156 unvisitedNeighbors.append(neighbor)157
158 return unvisitedNeighbors159
160 def highLight(self):161 self.cells[0].highLight()![]()
xxxxxxxxxx101# A demo of backtracking maze generator2
3from random import *4
5cols = rows = 206spots = []7cells = []8wallSpots = []9current = None10stack = []在程式的最開始,加入current作為backtracking演算法的現存位置,另外加入stack作為演算法的堆疊,用以紀錄演算法到過的地方。
xxxxxxxxxx51def setup():2 #(same as before)3 # start from the top left cell4 current = cells[0][0]5 current.visited = True在setup()的最低下加入current的位置,當然你也可以將current的初始位置隨機擺放。
xxxxxxxxxx161def draw():2 #(same as before)3 4 # display the current cell5 current.highLight()6 7 # generate the maze8 unvisitedNeighbors = current.checkNeighbors()9 if len(unvisitedNeighbors) > 0:10 next = choice(unvisitedNeighbors)11 stack.append(current)12 removeWall(current, next)13 next.visited = True14 current = next15 elif len(stack) > 0:16 current = stack.pop()在draw()的最底下,加入highlight(),highligt current這一格方便觀察。
之後便是核心的backtracking演算法,
找出
current所有未訪問的鄰居如果有未訪問的鄰居:
隨機挑選一個
將
current放入stack推疊將
current和next中間的牆拆去將
next標示為已訪問將
next變成current開始新一輪的操作
如果沒有未訪問的鄰居,即到達掘頭路
就將
stack推疊逐個釋放出來,直到上一個有鄰居(分岔路)的格。
xxxxxxxxxx121def removeWall(a, b):2 x = a.i - b.i3 y = a.j - b.j4
5 if x == 1: # a is on the right of b6 b.cells[1].wall = False7 if x == -1: # a is on the left of b8 a.cells[1].wall = False9 if y == 1: # a is below b10 b.cells[3].wall = False11 if y == -1: # a is above b12 a.cells[3].wall = False在setup()和draw()外加入removeWall()函數。由於所有牆都是cell的右方和下方,所以要分清楚這個兩cell哪一個在左右、哪一個在上下。
考考你
為程式加入上一章的AStar找尋路徑的演算法,做到跟我下面的程式一樣,先生成地圖再找路徑